However this population of cells is largely distinct from SOX2 GFP precursors that we have characterized here in embryonic and postnatal brain. There are links to more detailed descriptions which can be viewed in a week by week format.
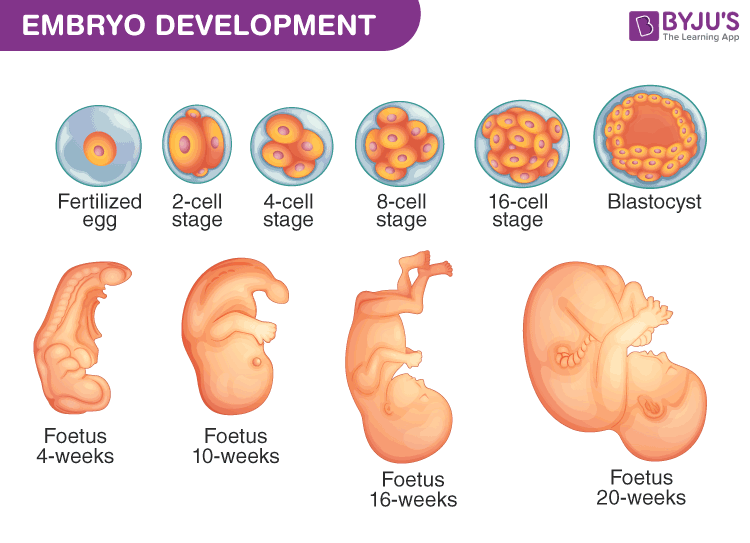
The number of embryonic cells increases but the overall size of the embryo stays the same.
. One into the processes of embryonic induction. 0925-4773930600 MOD 00158 Embryonic induction JMW. Activin A henceforth denoted as activin has been shown to be effective in inducing DE from hESCs and is a key induction factor used in many protocols 23However recent studies have shown that activin alone may not produce homogeneous differentiation and additional factors must be used to modulate supplementary.
Because mammalian embryos have no cytoplasmic determinants and have very small amounts of. Embryonic induction the influence of one group of cells on another group of cells plays a critical role in embryonic development. Embryonic induction consists of an interaction be-tween inducing and responding tissues that brings about alterations in the developmental pathway of the responding tissue.
This page shows some key events of human development during the embryonic period of the first eight weeks weeks 1 - 8 following fertilization. In 1924 Hans Spemann and Hilde Mangold transplanted a piece of tissue that influences the formation of the notochord and neural tube from the dorsal lip of an amphibian embryo to the ventral side of another amphibian embryo. 8 weeks - 10 gm.
This capability provides the basis for considering the ES cell system as a novel and unlimited source of cells for replacement therapies for the treatment of a. However this population of cells is largely distinct from SOX2 GFP precursors that we have characterized here in embryonic and postnatal brain. A the period during which the blastocyst moves down to the uterus and begins to implant in the lining.
HESC colonies p93 were plated onto the Matrigel layer with 1 mL mTeSR1 hESC media and supplement. Which of the following statements about fetal age and weight shows a normal relationship. Asked Feb 11 2016 in Psychology by Felipe.
From biology to cell therapy. Embryonic stem ES cells have the potential to develop into all cell types of the adult body. Cleavage divisions bring about considerable increase in the mass of protoplasm.
C the period during which the zygote is formed. The _____ is the embryonic stage which consists of an outer layer of epithelial cells and an internal water-filled cavity. This book aimed at experts and students alike offers a comprehensive review of the state of the art in both pancreatic development and regeneration.
Embryonic induction is best illustrated by which of the following a formation of the lens in the ectoderm after contact with the underlying optic cup b replacement of cartilage by bone c lysosomal action on the degenerating tail of a tadpole d development of the amnion surrounding the embryo e development of the mesoderm into the notochord. Cell Culture and Endoderm Induction. Which of the following statements best describes the process of cleavage in animal development.
Pluripotent human embryonic stem cells hESCs have both the unconstrained capacity for long-term stable undifferentiated growth in culture and the intrinsic potential for differentiation into all somatic cell types in the human body holding tremendous potential for restoring human tissue and organ function 13Derivation of hESCs essentially. The system of embryonic stem cell is known for its heterogeneity and stochasticity. Accepted 25 January 1993 The current.
Enamel of the teeth smooth muscle of the gut mucous lining of the larynx. BMP4 and BMP8 are secreted from extra embryonic ectoderm at E70 in mouse embryos. This review and commentary uses the induction of the lens of the eye and induction of the heart as examples to illustrate some of the processes involved in embryonic induction.
26 weeks - 1000 gm. Human pluripotent stem cells. Mechanisms of Development 41 1993 91-107 91 1993 Elsevier Scientific Publishers Ireland Ltd.
Differentiation of hESCs to DE. In the second cleavage division one of the two blastomeres usually divides a. In response to these factors competent cells at the posterior of the embryo will_____.
Slack Imperial Cancer Research Fund Developmental Biology Unit Department of Zoology University of Oxford Oxford UK Received 22 January 1993. The eye may be a window to the soul but for developmental biologists it has provided a window of another kind. This observation is best illustrated in the postnatal hippocampal field Figures Figures6EH 6 EH where an organized and widespread distribution of GFP cells contrasts with BLBP immunoreactivity that is.
Experiments on the self-regulation of embryonic development suggested ideas that changed over time as new technical advances allowed deeper levels of understanding of development at a physico-chemical level. Induction or cell-cell communication is one of the five essential developmental processes and occurs during development of all animal and plant species. Handling Data Variability.
Differences among biological repeats can occur in these cultures because of the use of different passages of ES cells or by spontaneous differentiation leading to substantial variation in between cells while still retaining similar trend towards specific. Genes with the dynamic pattern shown below are described at _______ genes and includes genes in the _______ pathway. The many strategies to differentiate adult and embryonic stem cells into pancreatic beta cells are also discussed in the context of potential therapeutic interventions for type I diabetes.
Induction is a prime example of extrinsic information that leads to different cell fates among initially identical cells. This observation is best illustrated in the postnatal hippocampal field Figures 6EH where an organized and widespread distribution of GFP cells contrasts with BLBP immunoreactivity that is concentrated only in the subicular area. Which of the following describes the embryonic period.
12 weeks - 200 gm. 20 weeks - 800 gm. 38 weeks - 4600 gm.
Human embryonic stem cells H1 cell line were cultured under feeder-free condition. This period is also considered the organogenic period when most organs within the embryo have begun to form. Which way does the WNT blow.
Which of the following structures is derived from paraxial mesoderm of the cervical region. Betacatenin signaling in hepatic development and progenitors. Which one of the following statements with regard to embryonic development in humans is correct.
6-well culture dishes were incubated with Matrigel coating hESC-qualified Matrix BD Biosciences San Jose CA USA for 30 minutes. Differentiation induction of mouse embryonic stem cells into sinus node-like cells by suramin. B the period during which the major organs and structures of the organism first develop.
Unraveling the induction of embryonic tissue differentiation 31 Self-regulation in development.

Day 7 13 23 Days Of Embryo After Successful Transfer Embryo Transfer Map Cavities

Embryo Development A Development Process Of Fetus Week By Week


0 Comments